ArrayList 源码解析
# 1、概念
- ArrayList 实现了 List 接口,所以List定义的方法都适用于ArrayList。
- ArrayList 底层是数组实现,所以每个ArrayList 对象创建后都有个初始化的容量,默认为10,数组在初始化之后就是固定的长度,容器内的元素不能超过当前的容量。
- 但ArrayList有自动扩容机制,当数组容量不够时,会进行扩容。这里的数组是一个Object类型的数组,可以容纳任何类型的对象。
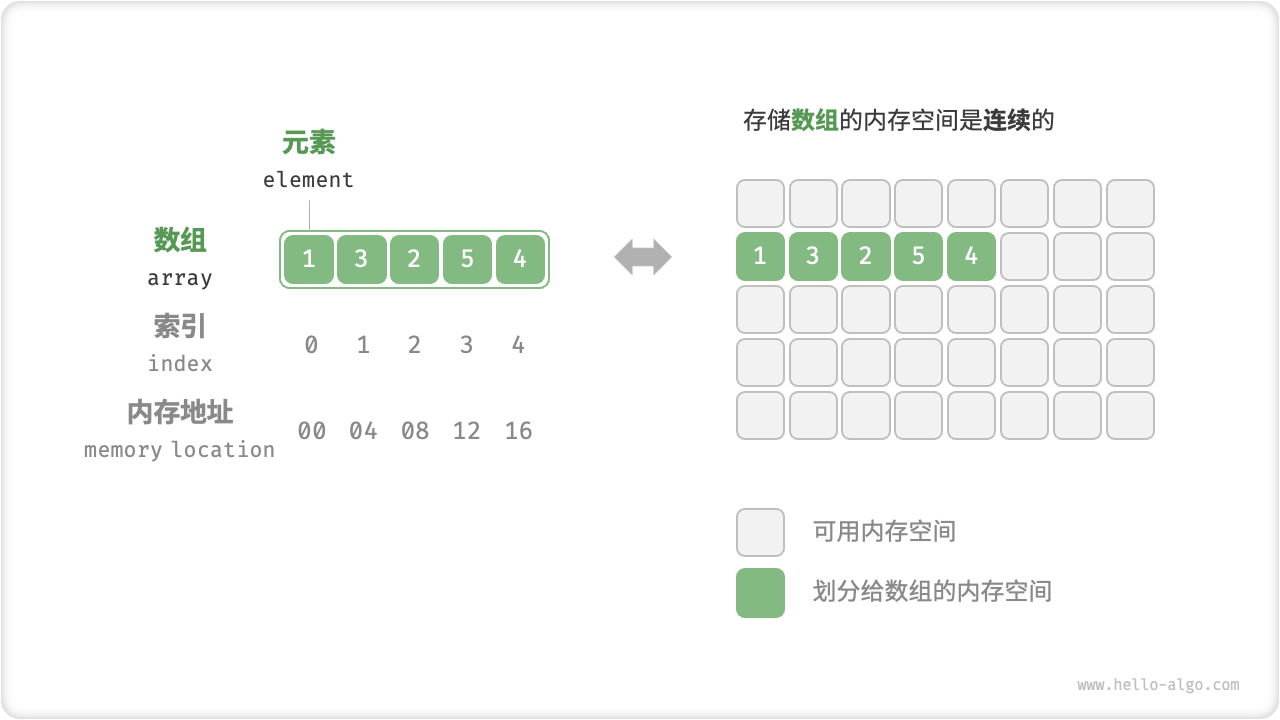
数组结构
源码
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
// ... ...
}
2
3
4
5
# 2、变量参数说明
ArrayList的实现,定义的一些变量参数。
源码
@java.io.Serial
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
参数变量说明
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| serialVersionUID | 这是一个用于序列化的版本号,用来确保序列化和反序列化过程中的版本一致性。 |
| DEFAULT_CAPACITY | 这是ArrayList的默认初始容量,即当没有指定容量时,会使用这个值作为初始容量:10。 |
| EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA | 这是一个共享的空数组实例,用于表示空的ArrayList实例。当ArrayList没有添加任何元素时,会使用这个空数组作为底层数组。 |
| DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA | 这也是一个共享的空数组实例,用于表示默认大小的空ArrayList实例。与EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA不同,当第一个元素被添加时,这个数组会被扩展为默认容量。 |
| elementData | 这是ArrayList的底层数组,用于存储ArrayList的元素。ArrayList的容量即为底层数组的长度。当elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA时,表示ArrayList是一个空的默认大小的实例,在添加第一个元素时会被扩展为默认容量。 |
| size | 这是ArrayList的大小,即它包含的元素数量。私有的size变量用于表示ArrayList的大小。 |
# 3、构造方法
ArrayList提供了多个构造方法,直接看源码。
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
if ((size = a.length) != 0) {
if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) {
elementData = a;
} else {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, size, Object[].class);
}
} else {
// replace with empty array.
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
- ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
可以设置一个初始容量,如果设置的容量小于0,则抛出异常。如果为0,就为默认空数组。
案例
ArrayList<Object> list = new ArrayList<>(20);
如果确认了List的长度,可以设置默认值,防止自动扩容,自动扩容是耗时操作。
- ArrayList()
构造一个空数组。默认为DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA。
案例
ArrayList<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
- ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c)
将集合作为参数传递给构造方法来创建一个新的ArrayList。
案例
// 创建一个包含整数的集合
List<Integer> collection = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
// 使用ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c)构造方法创建一个新的ArrayList
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(collection);
// 打印ArrayList中的元素
System.out.println("ArrayList元素:" + arrayList);
// 输出:ArrayList元素:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 4、扩容机制
我们现在知道ArrayList的底层是数组,数组是初始化确定后,长度就是不可变的。如果添加的数据长度大于数组的长度,就会报数组越界异常。 ArrayList就支持了自动扩容机制来解决这个问题,所以这就是为什么ArrayList是动态数组。
ArrayList的扩容机制:当数组容量不够时,会进行扩容,每次默认扩容为原来的1.5倍。数组进行扩容时,会重新申请内存空间,然后将原数组的数据拷贝到新数组中。这个操作的代价是很高的,空间和时间上都是很昂贵的。因此我们实际开发中尽量避免ArrayList的自动扩容。如果真的需要扩容,ArrayList提供了
ensureCapacity方法,这个方法是手动控制ArrayList的扩容,避免自动扩容。
下面直接看源码解析过程
- grow扩容方法
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
* @throws OutOfMemoryError if minCapacity is less than zero
*/
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (oldCapacity > 0 || elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity,
minCapacity - oldCapacity, /* minimum growth */
oldCapacity >> 1 /* preferred growth */);
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
} else {
return elementData = new Object[Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity)];
}
}
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(size + 1);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
记录原数组长度oldCapacity,然后调用ArraysSupport.newLength方法,这个方法是用来计算新数组的长度,返回值是新的数组长度。
- oldCapacity:原始容量,即当前ArrayList的容量。
- minCapacity - oldCapacity:需要增加的容量,即新元素的数量减去当前ArrayList容量。
- oldCapacity >> 1:oldCapacity的一半,即当前容量的一半,用于计算默认增长因子。
我们看一下newLength方法
public static int newLength(int oldLength, int minGrowth, int prefGrowth) {
// preconditions not checked because of inlining
// assert oldLength >= 0
// assert minGrowth > 0
int prefLength = oldLength + Math.max(minGrowth, prefGrowth); // might overflow
if (0 < prefLength && prefLength <= SOFT_MAX_ARRAY_LENGTH) {
return prefLength;
} else {
// put code cold in a separate method
return hugeLength(oldLength, minGrowth);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
最总返回长度为旧数组长度+最大扩容量,所以至少扩容原来数组的1.5倍。
- ensureCapacity手动扩容
ArrayList提供了ensureCapacity方法,可以手动扩容。调用的还是grop扩容方法。
源码
/**
* Increases the capacity of this {@code ArrayList} instance, if
* necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements
* specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > elementData.length
&& !(elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
&& minCapacity <= DEFAULT_CAPACITY)) {
modCount++;
grow(minCapacity);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 5、add()和addAll()
- ArrayList只提供了两个
add()公开方法,一个是直接数组最后新增元素,一个是指定位置新增。
- 数组最后新增元素,会判断是否需要扩容,数组长度超过会自动扩容。
- 数组指定位置新增元素,会判断数组是否越界,越界直接报
IndexOutOfBoundsException异常。
add()源码
/**
* This helper method split out from add(E) to keep method
* bytecode size under 35 (the -XX:MaxInlineSize default value),
* which helps when add(E) is called in a C1-compiled loop.
*/
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow();
elementData[s] = e;
size = s + 1;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
add(e, elementData, size);
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
modCount++;
final int s;
Object[] elementData;
if ((s = size) == (elementData = this.elementData).length)
elementData = grow();
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + 1,
s - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size = s + 1;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
- addAll()支持新增多个元素,也是提供了两种新增方式,末尾新增和指定位置新增。并且都支持自动扩容机制。
addAll()源码
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's Iterator. The behavior of this operation is
* undefined if the specified collection is modified while the operation
* is in progress. (This implies that the behavior of this call is
* undefined if the specified collection is this list, and this
* list is nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
modCount++;
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Object[] elementData;
final int s;
if (numNew > (elementData = this.elementData).length - (s = size))
elementData = grow(s + numNew);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, s, numNew);
size = s + numNew;
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the
* specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
modCount++;
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Object[] elementData;
final int s;
if (numNew > (elementData = this.elementData).length - (s = size))
elementData = grow(s + numNew);
int numMoved = s - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size = s + numNew;
return true;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
# 6、get()和set()
我们知道ArrayList底层是数组,所以对于数组,获取和设置元素就非常容易了,只要找到索引下标就行,也就是找到数组指定位置的内存地址就行,就能获取到值和设置值了。
源码
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
return elementData(index);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 7、remove()和removeAll()
- remove()提供了两种删除,指定位置删除和指定元素删除(第一次出现),指定元素删除需要满足
o.equals(elementData[index])的元素。删除元素之后后面的元素需要前移,为了让GC起作用,赋值了null,用于清除引用。
源码
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; //清除该位置的引用,让GC起作用
return oldValue;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
- removeAll() 是批量删除,是通过循环遍历删除。
源码
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return batchRemove(c, true, 0, size);
}
boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement,
final int from, final int end) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
final Object[] es = elementData;
int r;
// Optimize for initial run of survivors
for (r = from;; r++) {
if (r == end)
return false;
if (c.contains(es[r]) != complement)
break;
}
int w = r++;
try {
for (Object e; r < end; r++)
if (c.contains(e = es[r]) == complement)
es[w++] = e;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,
// even if c.contains() throws.
System.arraycopy(es, r, es, w, end - r);
w += end - r;
throw ex;
} finally {
modCount += end - w;
shiftTailOverGap(es, w, end);
}
return true;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# 8、indexOf()和lastIndexOf()
- indexOf()获取第一次出现的index,lastIndexOf()获取元素的最后一次出现的index:
源码
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# 9、trimToSize()
将ArrayList实例的容量修剪为列表的当前大小,也就是实际元素的大小。
源码
/**
* Trims the capacity of this {@code ArrayList} instance to be the
* list's current size. An application can use this operation to minimize
* the storage of an {@code ArrayList} instance.
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 10、Fail-Fast机制
Fail-Fast机制:快速失败机制,当使用迭代器遍历ArrayList时,迭代器会记录迭代开始时的modCount的值。如果在遍历过程中发现modCount的值发生了变化(有其他线程修改了ArrayList的结构),则会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常,通知遍历过程中的并发修改操作,从而避免产生不确定或错误的结果。
- modCount是一个用于记录对ArrayList的结构性修改次数的变量,每当ArrayList的结构发生改变时(如新增、删除或清空元素等操作),modCount的值都会自增。
源码
/**
* The number of times this list has been <i>structurally modified</i>.
* Structural modifications are those that change the size of the
* list, or otherwise perturb it in such a fashion that iterations in
* progress may yield incorrect results.
*
* <p>This field is used by the iterator and list iterator implementation
* returned by the {@code iterator} and {@code listIterator} methods.
* If the value of this field changes unexpectedly, the iterator (or list
* iterator) will throw a {@code ConcurrentModificationException} in
* response to the {@code next}, {@code remove}, {@code previous},
* {@code set} or {@code add} operations. This provides
* <i>fail-fast</i> behavior, rather than non-deterministic behavior in
* the face of concurrent modification during iteration.
*
* <p><b>Use of this field by subclasses is optional.</b> If a subclass
* wishes to provide fail-fast iterators (and list iterators), then it
* merely has to increment this field in its {@code add(int, E)} and
* {@code remove(int)} methods (and any other methods that it overrides
* that result in structural modifications to the list). A single call to
* {@code add(int, E)} or {@code remove(int)} must add no more than
* one to this field, or the iterators (and list iterators) will throw
* bogus {@code ConcurrentModificationExceptions}. If an implementation
* does not wish to provide fail-fast iterators, this field may be
* ignored.
*/
protected transient int modCount = 0;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
通过对modCount的检查,ArrayList保证了多线程环境下对集合的安全访问,提高了程序的健壮性。
# 11、ArrayList常用方法概览
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| add(E element) | 将指定的元素添加到ArrayList的末尾。 |
| add(int index, E element) | 在指定的索引位置插入指定的元素。 |
| addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 将指定集合中的所有元素添加到ArrayList的末尾。 |
| addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) | 将指定集合中的所有元素插入到指定的索引位置。 |
| remove(Object obj) | 移除ArrayList中首次出现的指定元素。 |
| remove(int index) | 移除指定索引位置的元素。 |
| clear() | 移除ArrayList中的所有元素。 |
| get(int index) | 返回指定索引处的元素。 |
| set(int index, E element) | 用指定的元素替换指定索引处的元素。 |
| size() | 返回ArrayList中的元素数量。 |
| isEmpty() | 判断ArrayList是否为空。 |
| contains(Object obj) | 判断ArrayList是否包含指定元素。 |
| indexOf(Object obj) | 返回首次出现指定元素的索引,如果不存在则返回-1。 |
| lastIndexOf(Object obj) | 返回最后一次出现指定元素的索引,如果不存在则返回-1。 |
| toArray() | 将ArrayList转换为一个数组。 |
| subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 返回指定范围内的元素作为一个新的List。 |
