PriorityQueue 源码解析
# 1、PriorityQueue概念
- PriorityQueue是优先队列,PriorityQueue实现了
Queue接口,不允许元素为null。 - 优先队列的作用是能保证每次取出的元素都是队列中权值最小的,Java默认是取最小的,也可以传入比较器。
- PriorityQueue是通过完全二叉树实现的小顶堆。而堆底层的实现还是数组。
PriorityQueue是有先后优先级的队列。
我们先来回顾一下完全二叉树和堆的概念,也可以去看看相关的一些数据结构和算法。
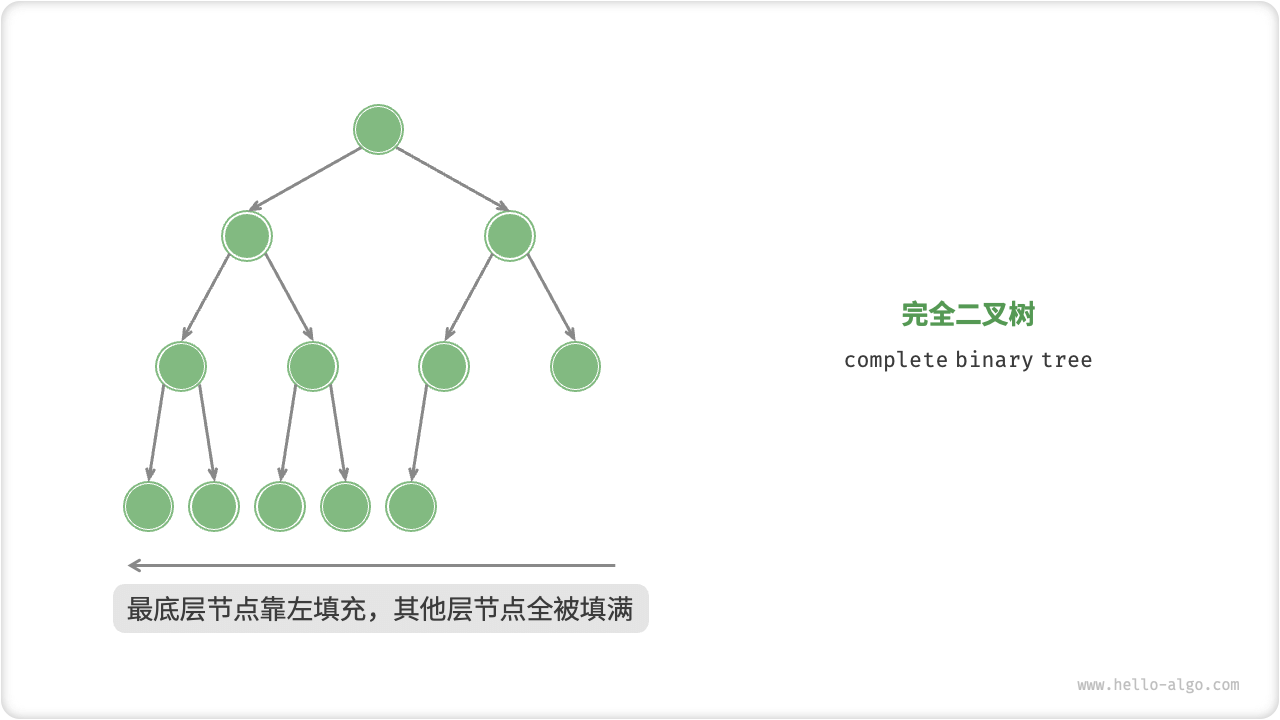
# 2、完全二叉树
完全二叉树(complete binary tree)是二叉树的其中一种,只有最底层的节点未被填满,且最底层节点尽量靠左填充。
完全二叉树结构
# 3、堆
堆(heap)是一种满足特定条件的完全二叉树,堆又分为大顶堆、小顶堆。
- 大顶堆:任意节点的值大于等于其子节点的值。
- 小顶堆:任意节点的值小于等于其子节点的值。
堆结构

# 5、PriorityQueue实现结构
完全二叉树实现的小顶堆,数组实现的优先队列。

通过如下公式计算某个节点的父节点以及子节点的下标
leftNo = parentNo*2+1
rightNo = parentNo*2+2
parentNo = (nodeNo-1)/2
2
3
# 5、PriorityQueue源码解析
PriorityQueue的peek()和element操作是常数时间,add(), offer(), 无参数的remove()以及poll()方法的时间复杂度都是log(N)。
源码
public class PriorityQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -7720805057305804111L;
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;
/**
* Priority queue represented as a balanced binary heap: the two
* children of queue[n] are queue[2*n+1] and queue[2*(n+1)]. The
* priority queue is ordered by comparator, or by the elements'
* natural ordering, if comparator is null: For each node n in the
* heap and each descendant d of n, n <= d. The element with the
* lowest value is in queue[0], assuming the queue is nonempty.
*/
transient Object[] queue; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The number of elements in the priority queue.
*/
private int size = 0;
/**
* The comparator, or null if priority queue uses elements'
* natural ordering.
*/
private final Comparator<? super E> comparator;
/**
* The number of times this priority queue has been
* <i>structurally modified</i>. See AbstractList for gory details.
*/
transient int modCount = 0; // non-private to simplify nested class access
// ...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
可以看到PriorityQueue内部的参数都是比较简单的,只有一个queue(数组存储)、size(元素个数)、comparator(比较器)、modCount(结构修改次数)。
# 5.1、构造函数
PriorityQueue提供了多个构造函数,可以根据需要选择合适的构造函数。
源码
/**
* Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} with the default initial
* capacity (11) that orders its elements according to their
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering}.
*/
public PriorityQueue() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, null);
}
/**
* Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} with the specified initial
* capacity that orders its elements according to their
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering}.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity for this priority queue
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code initialCapacity} is less
* than 1
*/
public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, null);
}
/**
* Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} with the default initial capacity and
* whose elements are ordered according to the specified comparator.
*
* @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this
* priority queue. If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable
* natural ordering} of the elements will be used.
* @since 1.8
*/
public PriorityQueue(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, comparator);
}
/**
* Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} with the specified initial capacity
* that orders its elements according to the specified comparator.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity for this priority queue
* @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this
* priority queue. If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable
* natural ordering} of the elements will be used.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code initialCapacity} is
* less than 1
*/
public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity,
Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
// Note: This restriction of at least one is not actually needed,
// but continues for 1.5 compatibility
if (initialCapacity < 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.comparator = comparator;
}
/**
* Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} containing the elements in the
* specified collection. If the specified collection is an instance of
* a {@link SortedSet} or is another {@code PriorityQueue}, this
* priority queue will be ordered according to the same ordering.
* Otherwise, this priority queue will be ordered according to the
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} of its elements.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed
* into this priority queue
* @throws ClassCastException if elements of the specified collection
* cannot be compared to one another according to the priority
* queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection or any
* of its elements are null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public PriorityQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {
if (c instanceof SortedSet<?>) {
SortedSet<? extends E> ss = (SortedSet<? extends E>) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) ss.comparator();
initElementsFromCollection(ss);
}
else if (c instanceof PriorityQueue<?>) {
PriorityQueue<? extends E> pq = (PriorityQueue<? extends E>) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) pq.comparator();
initFromPriorityQueue(pq);
}
else {
this.comparator = null;
initFromCollection(c);
}
}
/**
* Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} containing the elements in the
* specified priority queue. This priority queue will be
* ordered according to the same ordering as the given priority
* queue.
*
* @param c the priority queue whose elements are to be placed
* into this priority queue
* @throws ClassCastException if elements of {@code c} cannot be
* compared to one another according to {@code c}'s
* ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified priority queue or any
* of its elements are null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public PriorityQueue(PriorityQueue<? extends E> c) {
this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) c.comparator();
initFromPriorityQueue(c);
}
/**
* Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} containing the elements in the
* specified sorted set. This priority queue will be ordered
* according to the same ordering as the given sorted set.
*
* @param c the sorted set whose elements are to be placed
* into this priority queue
* @throws ClassCastException if elements of the specified sorted
* set cannot be compared to one another according to the
* sorted set's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified sorted set or any
* of its elements are null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public PriorityQueue(SortedSet<? extends E> c) {
this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) c.comparator();
initElementsFromCollection(c);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
可以看到PriorityQueue提供的方法还是比较简单的,有可以传入比较器的,也有可以设置初始化数组大小的。
# 5.2、add()和offer()
add(E e)和offer(E e)的语义相同,都是向优先队列中插入元素,只是Queue接口规定二者对插入失败时的处理不同,前者在插入失败时抛出异常,后则则会返回false。对于PriorityQueue这两个方法其实没什么差别。
插入过程
和offer().3dbfa7c9.png)
新加入的元素可能会破坏小顶堆的性质,因此需要进行必要的调整。
源码
//offer(E e)
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)//不允许放入null元素
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow(i + 1);//自动扩容
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0)//队列原来为空,这是插入的第一个元素
queue[0] = e;
else
siftUp(i, e);//调整
return true;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
上述代码中,扩容函数grow()类似于ArrayList里的grow()函数,就是再申请一个更大的数组,并将原数组的元素复制过去,这里不再赘述。需要注意的是siftUp(int k, E x)方法,该方法用于插入元素x并维持堆的特性。
源码
//siftUp()
private void siftUp(int k, E x) {
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;//parentNo = (nodeNo-1)/2
Object e = queue[parent];
if (comparator.compare(x, (E) e) >= 0)//调用比较器的比较方法
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = x;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
新加入的元素x可能会破坏小顶堆的性质,因此需要进行调整。调整的过程为:从k指定的位置开始,将x逐层与当前点的parent进行比较并交换,直到满足x >= queue[parent]为止。注意这里的比较可以是元素的自然顺序,也可以是依靠比较器的顺序。
# 5.3、element()和peek()
element()和peek()的语义完全相同,都是获取但不删除队首元素,也就是队列中权值最小的那个元素,二者唯一的区别是当方法失败时前者抛出异常,后者返回null。根据小顶堆的性质,堆顶那个元素就是全局最小的那个;由于堆用数组表示,根据下标关系,0下标处的那个元素既是堆顶元素。所以直接返回数组0下标处的那个元素即可。
获取堆顶元素
和peek().3c6530b4.png)
源码
//peek()
public E peek() {
if (size == 0)
return null;
return (E) queue[0];//0下标处的那个元素就是最小的那个
}
2
3
4
5
6
# 5.4、remove()和poll()
remove()和poll()方法的语义也完全相同,都是获取并删除队首元素,区别是当方法失败时前者抛出异常,后者返回null。由于删除操作会改变队列的结构,为维护小顶堆的性质,需要进行必要的调整。
删除过程
和poll().ae141753.png)
源码
public E poll() {
if (size == 0)
return null;
int s = --size;
modCount++;
E result = (E) queue[0];//0下标处的那个元素就是最小的那个
E x = (E) queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
if (s != 0)
siftDown(0, x);//调整
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
上述代码首先记录0下标处的元素,并用最后一个元素替换0下标位置的元素,之后调用siftDown()方法对堆进行调整,最后返回原来0下标处的那个元素(也就是最小的那个元素)。重点是siftDown(int k, E x)方法,该方法的作用是从k指定的位置开始,将x逐层向下与当前点的左右孩子中较小的那个交换,直到x小于或等于左右孩子中的任何一个为止。
源码
//siftDown()
private void siftDown(int k, E x) {
int half = size >>> 1;
while (k < half) {
//首先找到左右孩子中较小的那个,记录到c里,并用child记录其下标
int child = (k << 1) + 1;//leftNo = parentNo*2+1
Object c = queue[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < size &&
comparator.compare((E) c, (E) queue[right]) > 0)
c = queue[child = right];
if (comparator.compare(x, (E) c) <= 0)
break;
queue[k] = c;//然后用c取代原来的值
k = child;
}
queue[k] = x;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 5.5、remove(Object o)
remove(Object o)方法用于删除队列中跟o相等的某一个元素(如果有多个相等,只删除一个),该方法不是Queue接口内的方法,而是Collection接口的方法。由于删除操作会改变队列结构,所以要进行调整;又由于删除元素的位置可能是任意的,所以调整过程比其它函数稍加繁琐。具体来说,remove(Object o)可以分为2种情况:1. 删除的是最后一个元素。直接删除即可,不需要调整。2. 删除的不是最后一个元素,从删除点开始以最后一个元素为参照调用一次siftDown()即可。此处不再赘述。
删除过程

源码
//remove(Object o)
public boolean remove(Object o) {
//通过遍历数组的方式找到第一个满足o.equals(queue[i])元素的下标
int i = indexOf(o);
if (i == -1)
return false;
int s = --size;
if (s == i) //情况1
queue[i] = null;
else {
E moved = (E) queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
siftDown(i, moved);//情况2
......
}
return true;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
